Round
When we think of love, marriage and proposals, it’s the round diamond engagement ring that first comes to mind. The round brilliant is the most popular diamond shape, representing almost 75% of diamonds sold in the engagement ring market.
When we think of love, marriage and proposals, it’s the round diamond engagement ring that first comes to mind. The round brilliant is the most popular diamond shape, representing almost 75% of diamonds sold in the engagement ring market.
Best known for its brilliance, the round diamond has 58 angular facets divided amongst its crown, girdle and pavillion. Facets are the surfaces of a diamond that can be polished in order to refract and bounce light from the bottom of the diamond, back through the top, giving it unbelievable sparkle and brightness.
Also known as round brilliant, these diamonds have an iconic reputation, one that’s sure to impress.
Round diamond engagement rings have become an iconic, time-honored engagement tradition. It’s versatile circular shape that suits all styles and metals.
Round brilliant diamonds are the most popular shape for engagement rings, representing almost 75% of diamonds sold worldwide.
| Among our customers, over 50% choose a round diamond as their centre stone.
Iconic stars are also sporting round diamonds, with celebrities like Miranda Kerr and Rosie Huntington-Whitely both wearing round diamond engagement rings, one with tapered diamond baguette side stones, while the other is set on a simple diamond pavé band.
The popularity of a round brilliant diamond, paired with the amount of waste produced during its cutting process, does mean that these diamonds carry the highest premium.
A cut grade is exclusively given to round diamonds–and is the most important factor to consider when choosing a round shape.
For the greatest brilliance and fire, we recommend (and only offer) very good and excellent cut grades for round brilliant diamonds.
This term refers to the diamond’s proportions–specifically how the diamond facets interact with the light.
Hundreds of years have gone into perfecting the cutting process of round diamonds. For centuries, diamond cutters have followed scientific theories of light reflection in order to maximise the round diamond’s fire and brilliance.
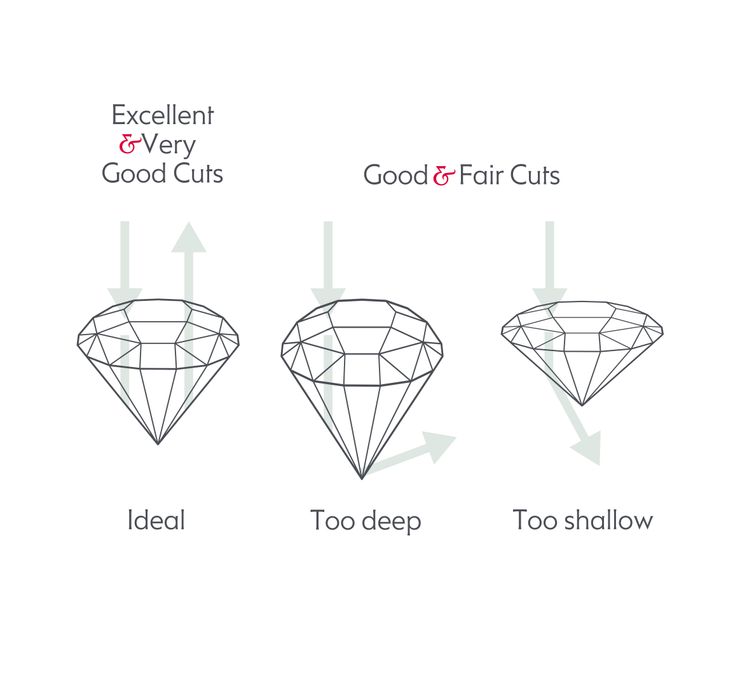
The Gemmological Institute of America (GIA) then spent decades refining and developing a cut grading system for round brilliant diamonds, which emphasises the significance of the round brilliant diamond and its reputation.
The table below serves as a general guideline for determining the cut grade of a round diamond. GIA takes these and other factors into consideration when assigning a cut grade.
| Excellent | Very Good | Good | Fair | Poor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table % | 53-58 | 52-53 or 58-60 | 51 or 61-64 | 50 or 65-69 | <50 or >69 |
| Depth % | 59-62.3 | 58-58.9 or 62.4-63.5 | 57.5-57.9 or 63.6-64.1 | 56.5-57.4 or 64.2-65 | <56.5 or >65 |
| Crown Angle | 34-34.9 | 32.1-33.9 or 35-35.5 | 30.1-32 or 36-37.9 | 29-30 or 38-40.5 | <29 or >40.5 |
| Pavillion Depth | 42.8-43.2 | 42-42.7 or 43.3-43.9 | 41-41.9 or 44-45.5 | 39-40.9 or 45.6-48 | <39 or >48 |
| Girdle | Thin to Slightly Thick | Very Thin to Slightly Thick | Very Thin to Thick | Very Thin to Very Thick | Ex. Thin to Ex. Thick |
| L/W Ratio | 1.00-1.01 | 1.00-1.01 | 1.00-1.01 | 1.02 | >1.02 |
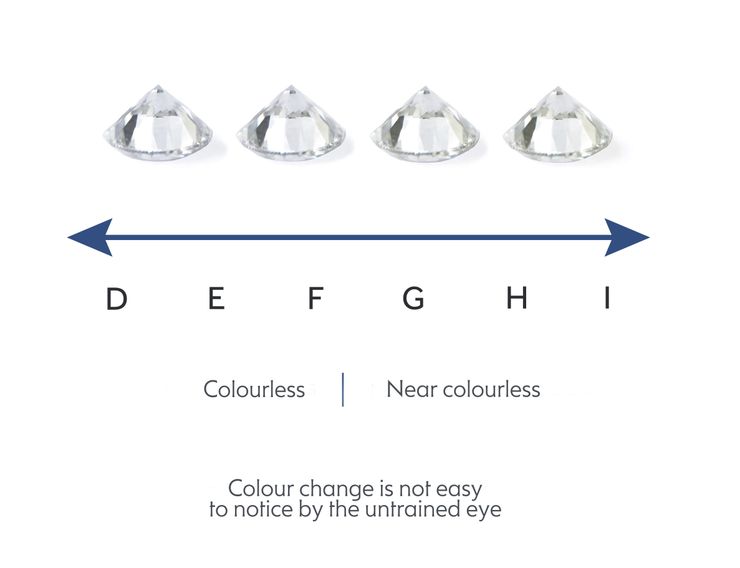
Evaluating colour in round diamonds is entirely dependent on the preference of its buyer or wearer.
Customers sometimes prefer the warmer tones of colour grades G-H to the rare, icy cool tones of colour grades D-F, especially when set in rose or yellow gold.
The truth is, the difference between these two colour grade ranges is difficult to perceive in round diamonds, especially to the naked eye.
| Excellent | Very Good | Good | |
|---|---|---|---|
| < 0.50ct | D-G | H-I | J-K |
| 0.51-1.00ct | D-G | H-I | J-K |
| 1.00-2.00ct | D-F | G-H | I-J |
| >2.00ct | D-F | G | H |
Again, clarity is dependent on personal preference. When diamonds are formed deep in the earth, they develop clarity characteristics–slight irregularities visible under 10x magnification. Depending on the size, quantity, placement, tone or colour of these clarity characteristics, they may or may not be visible to the naked eye. This is one of the reasons why a truly flawless diamond is so rare.
Some people may be entirely comfortable with a diamond that features many clarity characteristics that aren’t visible to the naked eye, while others may insist on a technically flawless appearance.
To ensure the brilliance and fire that makes diamonds so enchanting, we offer SI1 clarity grades or higher.
| Excellent | Very Good | Good | |
|---|---|---|---|
| < 0.50ct | FL - VS2 | SI1 - SI2 | I1 |
| 0.51-1.00ct | FL - VS1 | VS2 - SI1 | SI2 |
| 1.00ct - 2.00ct | FL - VSS2 | VS1 -VS2 | SI1 - SI2 |
| > 2.00ct | FL - VVS2 | VS1 - VS2 | SI1 |